Technical

Ceramic surfaces: different sizes, same average quartz content | by Alessandro Filipponi
(April 2025) | The beauty, variety and versatility of ceramic tiles make them a key material in both interior design and construction. Whether used as large panels or slabs to clad entire spaces or in smaller formats for decorative detailing, one question often arises: does the mineral composition vary with size? The answer is no, particularly in the case of one essential component: quartz.
Crystalline silica, whose most common mineral form is quartz, occurs naturally in ceramic raw materials such as clay, kaolin and feldspar. It is an essential component that ensures dimensional stability during firing and improves mechanical strength.
Quartz content
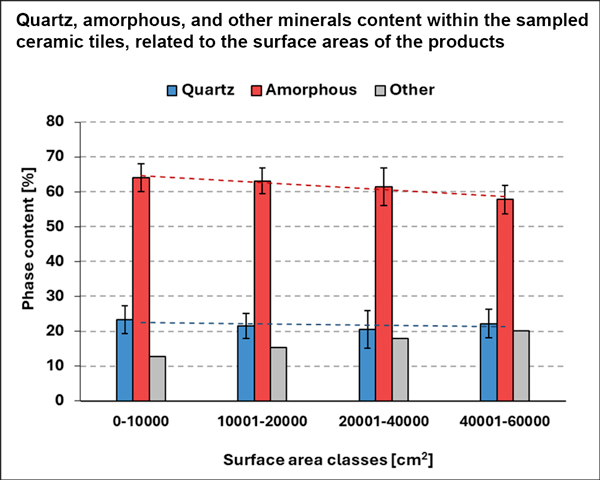
A study conducted in collaboration with the University of Bologna, the University of Modena and Reggio Emilia and Italy’s National Research Council (CNR) found that quartz content remains consistent across tile sizes, ranging from 8% to 30% with an average of 23%, regardless of surface area or thickness. In other words, large slabs and small tiles alike contain almost identical average quantities of quartz.
Principal component
The same study identified the amorphous (or glassy) phase as the principal component of Italian ceramic tiles, accounting for between 54% and 70% of the total composition (average 63%). This phase incorporates all constituents of the ceramic material and plays a crucial role in developing the technical properties of the finished product.
From a safety standpoint, current knowledge indicates that the amorphous phase poses no health risks. On the contrary, some scientific studies suggest it may help mitigate risks associated with crystalline silica.
Focus on safety
The health risks associated with crystalline silica derive exclusively from the inhalation of fine crystalline dust particles (known as respirable crystalline silica) produced during machining operations such as cutting. For this reason, workers must adopt appropriate safety measures, including the use of wet cutting techniques and personal protective equipment.